Table Of Content
In the case of a teratoma, your unspecialized germ cells turn into different types of specialized cells (like hair cells, muscle cells and bone cells). That’s why a teratoma contains a collection of seemingly random body parts and tissues. An epidermoid (say "eh-pih-DER-moyd") cyst is a lump just under the skin. These cysts can form when a hair follicle becomes blocked.
Benign and malignant cysts
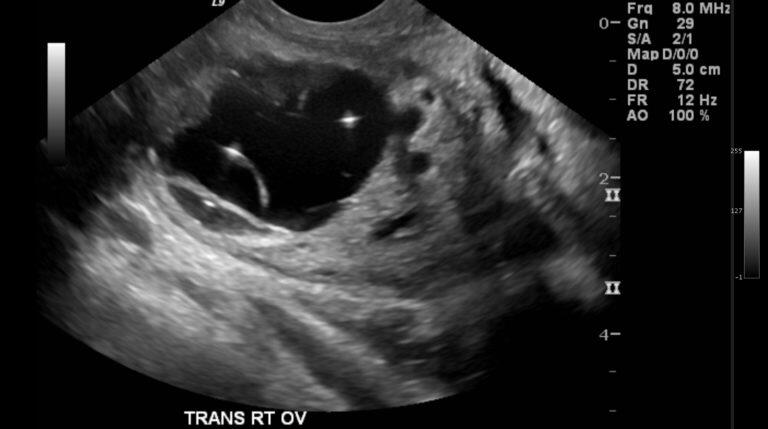
If people experience symptoms of any complications, they should seek prompt medical attention. They may also order imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI scan. They most commonly affect the ovary on the right side, but in 12% of cases, they can develop on both ovaries.
What if my provider finds a teratoma on the fetus during pregnancy?
Doctors remove huge hairball growing inside 30-year-old woman's ovaries since birth - The Mirror
Doctors remove huge hairball growing inside 30-year-old woman's ovaries since birth.
Posted: Fri, 31 Jan 2020 08:00:00 GMT [source]
An opposing theory explains the fetus in fetu as merely a more developed dermoid cyst. But the high level of development favors the twin theory. Some of these primitive germ cells become your sperm- and egg-producing cells. But germ cells can also be found elsewhere in the body, especially in the region of the tailbone and the mediastinum (a membrane separating the lungs). A symptom of ovarian teratoma is intense pain in the pelvis or abdomen.
action: 'healthbeat'
In some cases, it can be done without removing the ovary. Diagnosing a periorbital dermoid cyst or a similar cyst near the skin’s surface in the neck or chest can usually be done with a physical exam. Your doctor may be able to move the cyst under the skin and get a good sense of its size and shape.
Scheduling regular pelvic exams and speaking with your provider about any symptoms you may be experiencing can help prevent any problems with a cyst. When they’re located in and around the face and neck, they can cause noticeable swelling under the skin. One of the main concerns with a dermoid cyst is that it can rupture and cause an infection of the surrounding tissue.
A mom said she had a cyst with teeth and hair in her uterus. It's not as rare as you might think.
Anyone with ovaries can develop an ovarian dermoid cyst. They’re likely present at birth, but they’re usually not discovered until a routine imaging procedure. It’s not uncommon, for instance, to learn during a pregnancy ultrasound that you have this type of cyst. Teratomas are thought to originate in utero, so can be considered congenital tumors. Many teratomas are not diagnosed until much later in childhood or in adulthood.
How is a dermoid cyst treated?
They’re the most common type of ovarian tumor found during pregnancy. About one-third of all benign tumors diagnosed during pregnancy are ovarian dermoid cysts. A teratoma is a rare type of germ cell tumor that may contain immature or fully formed tissue, including teeth, hair, bone and muscle. Most teratomas are benign (noncancerous) but they can be malignant (cancerous).
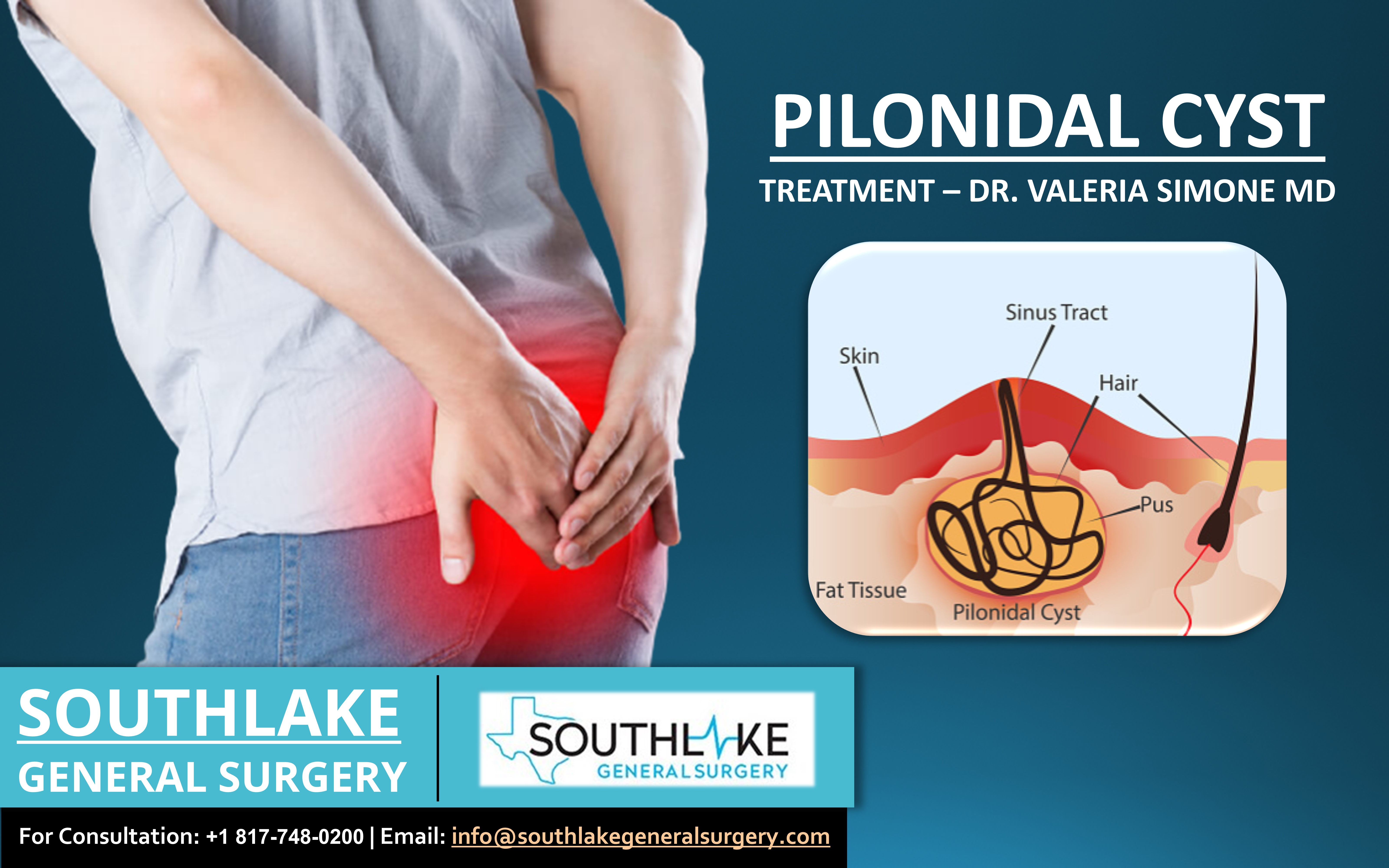
This allows skin cells and other materials to collect in a sac near the skin’s surface. Because the glands that are in the cyst continue to secrete fluids, the cyst continues to grow. Dermoid cysts are caused when skin and skin structures become trapped during fetal development.
Dentigerous cysts surround the crown of an unerupted tooth. It typically develops when a person is in their 20s and 30s, though it can happen at other times too. An inflammatory reaction can occur if a dermoid cyst is disrupted, and the cyst can recur if it is not completely excised.
They are common in acne and may occur on the face, neck, back, and genitals. These cysts are not cancer and do not lead to cancer. They tend not to hurt, but they can sometimes become swollen and painful. They also may break open (rupture) and cause scarring. Functional cysts are the most common type of ovarian cyst and aren’t disease-related.
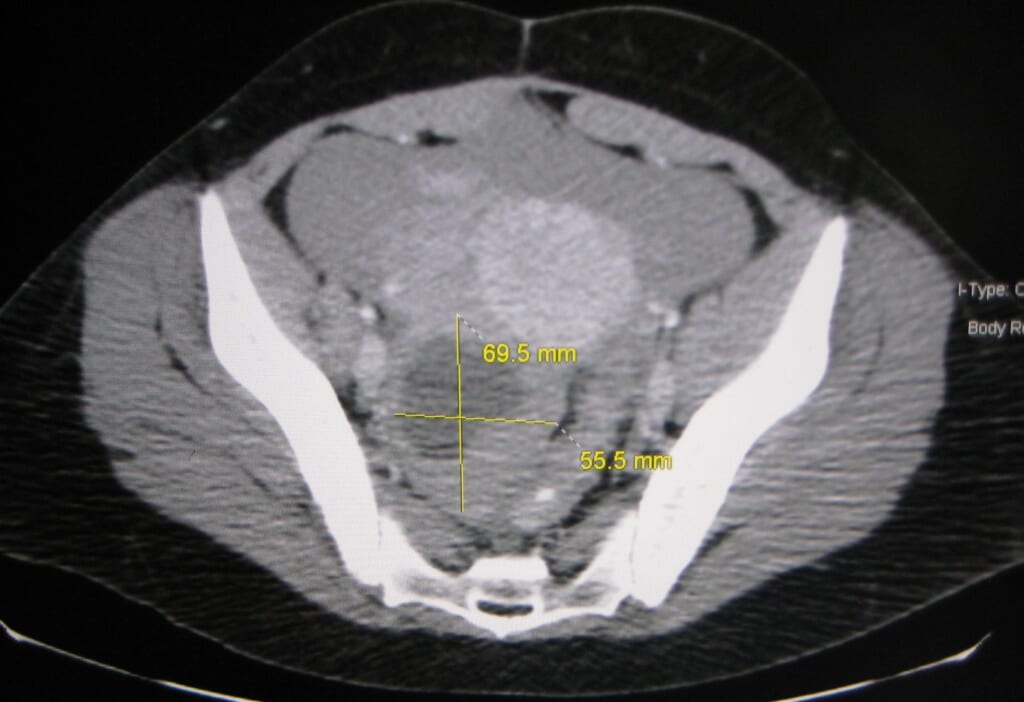
A healthcare professional may request a further evaluation if the cyst measures more than 10 cm and is complex. Complex cysts are filled with either blood or hard substances. Sometimes, a doctor can drain, or aspirate, the cyst by inserting a needle or catheter into the cavity. If the cyst is not easily accessible, they may use radiologic imaging to accurately guide the needle or catheter. A person may also experience headaches and other symptoms if a cyst develops on the brain.
If the egg isn't fertilized, it's simply reabsorbed by the body — perhaps before it even reaches the uterus. About two weeks later, the lining of the uterus sheds through the vagina. People should seek prompt medical help if complications develop.
Ovarian dermoid cysts aren’t cancerous, but they can cause complications if they grow too large. A healthcare provider can evaluate your cyst and advise on whether to remove it. "Rarely, a dermoid cyst can rupture causing a severe, sharp tummy pain which may make you double over," she explains.
Torsion, the most common complication, can be avoided with surgical cyst removal. Most dermoid cysts remain asymptomatic and won't impact fertility in themselves. Small, asymptomatic ovarian dermoid cysts may be discovered incidentally during routine ultrasound exams, such as those given during pregnancy.
Your provider can often remove a dermoid cyst through surgery. Cyst removal can reduce the chance of having symptoms in the future. Sometimes, these layers grow atypically, with mature tissue bunching together to form a dermoid cyst. The cyst may contain hair and teeth, but it may also include tissue that arises from any of the three layers that make up a germ cell.
This increases the chance of painful twisting of the ovary, called ovarian torsion. Ovarian torsion may reduce or stop blood flow to the ovary. A doctor may recommend surveillance if the cyst is small and not causing any symptoms. A doctor often discovers the presence of an ovarian dermoid cyst during examinations for other conditions. The cysts become filled with hair, teeth, fat, and bone as the trapped cells grow into mature tissue.